You have likely heard everything about the Windows 11 operating system. Numerous individuals you know have taken advantage of the free upgrade to Windows 11 and either adore or despise it. You are now looking forward to trying it out. You have discovered that when you try to upgrade to Windows 11, you receive an error message stating that your processor is not supported. What can you do?
While the error prompts many users to purchase a new computer, it is possible to bypass it and install Windows 11 regardless.
Should You Install Windows 11 on an Unsupported Processor?
Each computer is unique, and the reasons for Windows 11 incompatibility may vary from system to system. Even Windows 7 computers that meet all hardware compatibility requirements can be upgraded.
The most common reason your system does not meet the “minimal system requirements to run Windows 11” is an incompatible CPU. Check Microsoft’s lists of supported Intel and AMD processors to determine if yours is supported.
You can verify this by opening Windows Settings and selecting Windows Update from the menu on the left.
You will likely see a red X next to the message “This computer does not meet the minimum system requirements to run Windows 11.”
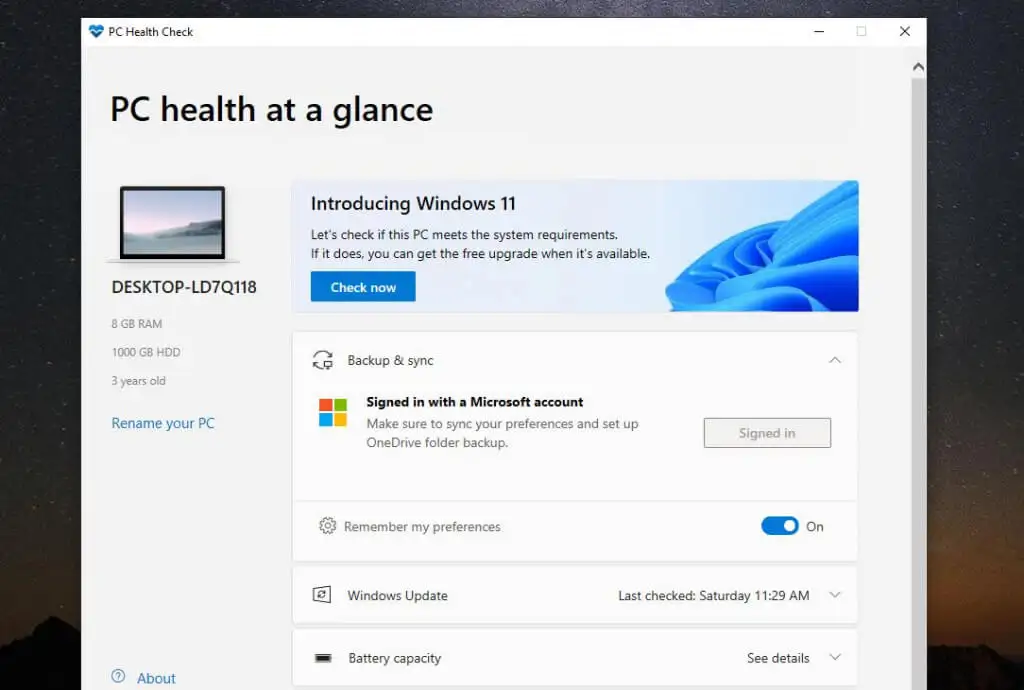
Utilizing the PC Health Check Software
This is followed by a link to the PC Health Check application. This tool will scan your computer and identify the reasons why it is incompatible with Windows 11.
To initiate the scan, select the Check now button when you first launch the tool.
After it completes, the message that your system does not meet the minimum hardware requirements will appear again. But this time, it will list the primary incompatibility reason.
The most likely cause for your system is “The processor is not currently supported by Windows 11.”
If you select See all results, additional reasons why your system may not be compatible with Windows 11 will be displayed. This could include TPM 2.0, RAM availability, Secure Boot, or your CPU.
You can enable Secure Boot settings in your BIOS by switching from “Legacy” BIOS to UEFI/BIOS as the PC’s boot mode. Note that this only applies if your BIOS supports this feature.
Additionally, you will see where your system IS compatible. Hopefully, the incompatibility of your system is limited to the processor and nothing else. Ideally, your system should support at least TPM 2.0. Nevertheless, you should still be able to install Windows 11 if you so choose.
Important: If you do not have at least 4 GB of RAM, you will not be able to install Windows 11 using the workaround outlined in this article.
Should Windows 11 be Installed on an Incompatible Computer?
If your system’s incompatibility with Windows 11 is limited to the CPU and no other unsupported hardware, you have the least chance of encountering issues when upgrading to Windows 11. However, risks are not entirely absent.
According to Microsoft, those who install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware will not receive Windows 11 updates.
Microsoft also claims: “Installing Windows 11 on this PC is not recommended and may cause compatibility issues.” If you install Windows 11, your PC will no longer be supported and will no longer be eligible for updates. Damages caused by incompatibility are not covered by the manufacturer’s warranty.”
These “damages” may increase the likelihood of Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) errors, as well as freezing or crashing of your computer.
What Regarding TPM 2.0?
Windows 11 can still be installed even if the list of incompatibilities includes the absence of Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0. However, some additional security risks will be assumed.
TPM is a physical chip present in the majority of modern computers that prevents the execution of malicious software (malware). If your computer does not have TPM 2.0 enabled, it is possible that it still has the feature. Simply enable TPM in the BIOS or purchase a TPM module.
Should I Upgrade to Windows 11 Anyway? (Windows 11 Showing Your Processor is Not Supported)
This indicates that there are no obstacles to upgrading to Windows 11 using this guide. If you decide to switch to this new operating system, however, you will assume a certain level of risk. Your system may no longer receive Windows updates, and BSoD errors may increase.
Many computers that remain on Windows 10 may begin to experience problems receiving more recent security updates regardless. This author, for instance, encountered an endless update cycle in which Windows 10 updates failed and had to be uninstalled each time the computer was restarted.
You have nothing to lose by upgrading to this new version of Windows on an incompatible device and taking advantage of all its new features. It will prevent you from purchasing a new computer for at least another year or two.
How to Upgrade an Incompatible Computer to Windows 11
If you have decided to upgrade to Windows 11 despite Microsoft’s warnings, the process is relatively straightforward.
Download the ISO File for Windows 11 (Windows 11 Showing Your Processor is Not Supported)
Downloading the Windows 11 ISO file from Microsoft’s website is the first step. Please be aware that this installation is only compatible with 64-bit processors. Also, if you’re upgrading to a fully licensed Windows 10 PC, you won’t have to worry about Windows 11 activation issues.
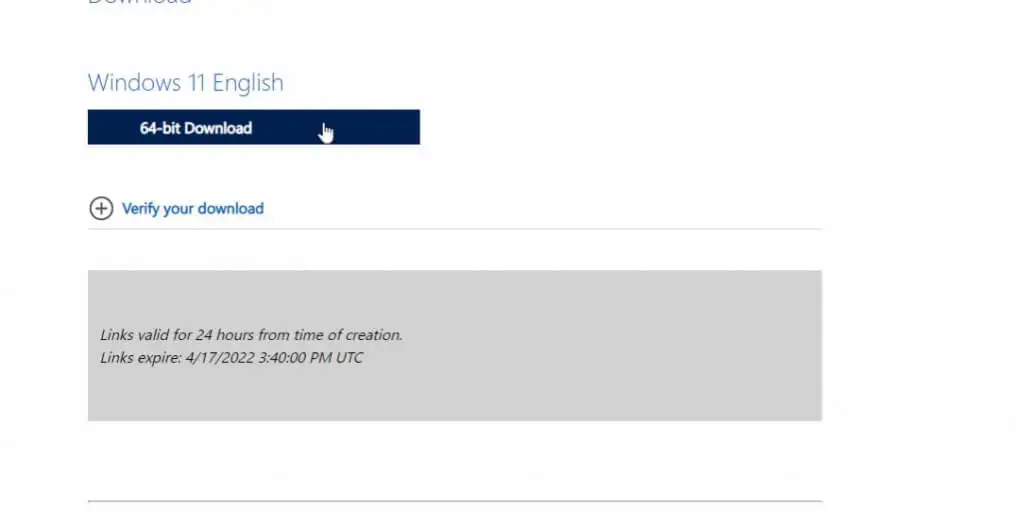
- Download Windows 11 from Microsoft’s website. Select Windows 11 from the drop-down menu and then click the Download button in the Download Windows 11 Disk Image (ISO) section.
- An additional language selection section will appear below this. Select your preferred language and click the Confirm button.
- Finally, the 64-bit Download button will be displayed. To download the Windows 11 ISO file to your hard drive, select this option.
Modify the Registry to Install Windows 11 (Windows 11 Showing Your Processor is Not Supported)
Installing Windows 11 on an incompatible system requires the addition of a registry entry.
- Enter regedit into the Start menu and select the Registry Editor.
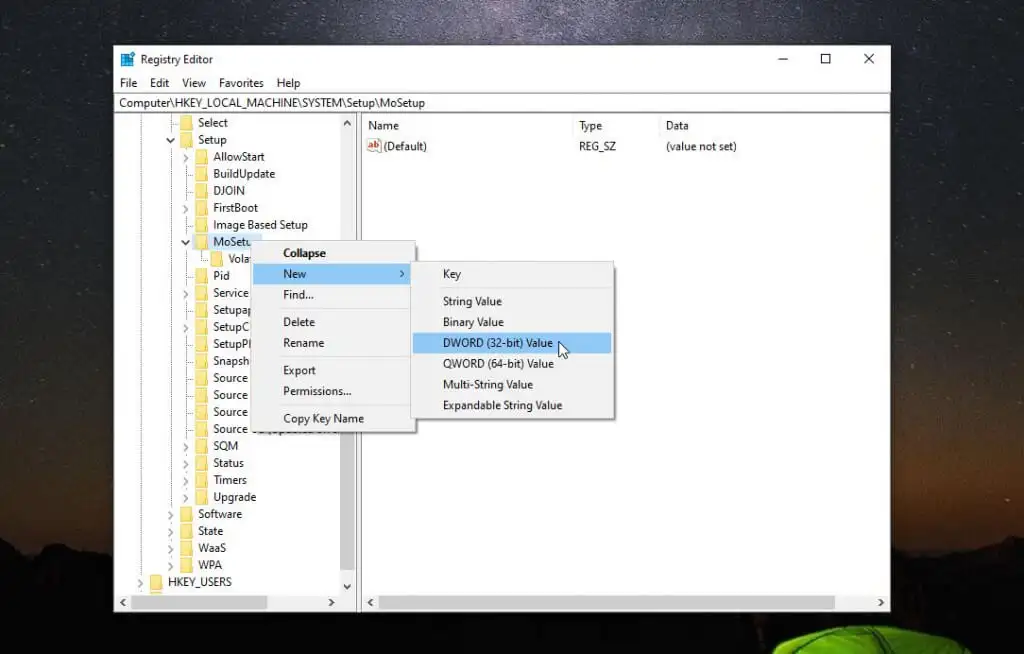
- Upon the launch of the editor, navigate to ComputerHKEY LOCAL MACHINESYSTEMSetupMoSetup.
- Select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value by right-clicking the MoSetup folder.
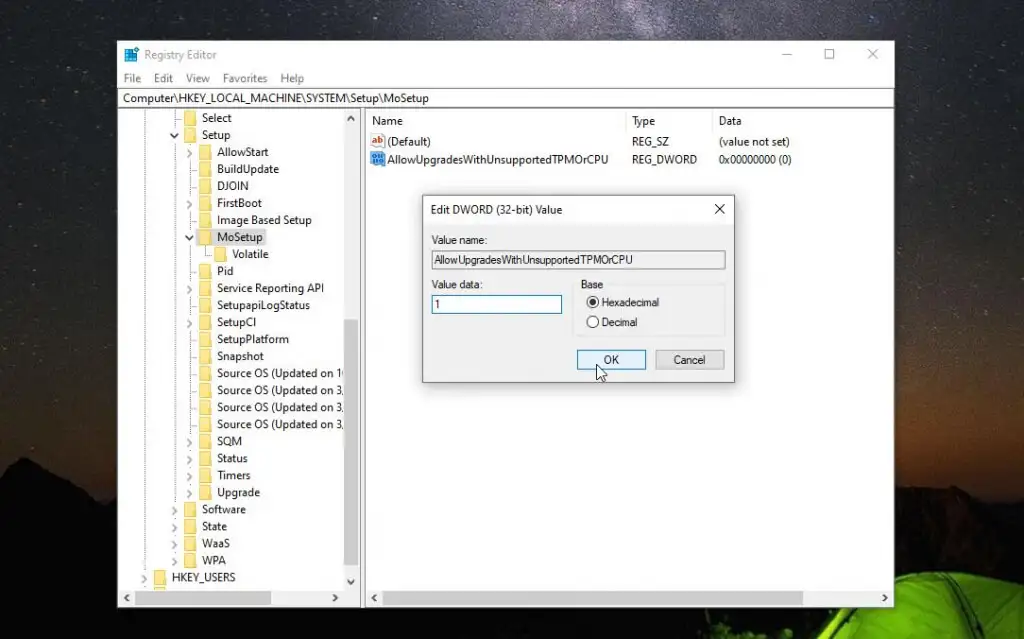
- Reference this property as AllowUpgradesWithUnsupportedTPMOrCPU. Double-click the newly created value and enter 1 in the Value field. Select OK when finished.
At this point, you can close the registry editor. You are now prepared to upgrade to Windows 11.
ISO File-Based Windows 11 Installation
Once the ISO file has been completely downloaded, follow the steps below to upgrade to Windows 11.
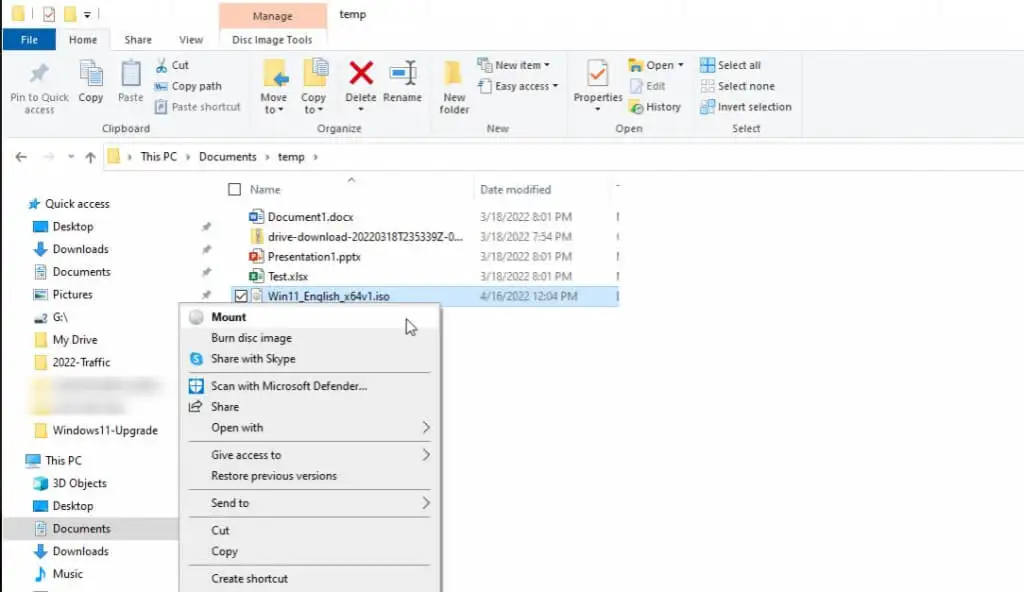
- Right-click on the ISO file and choose Mount.
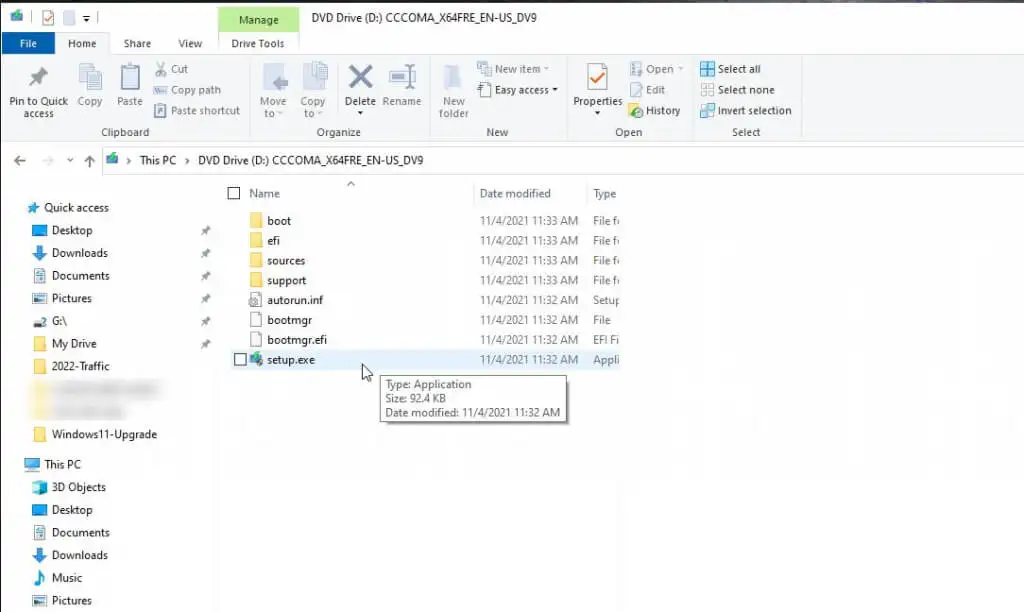
- This mounts a new drive within File Explorer. Double-click the setup.exe file located on that drive.
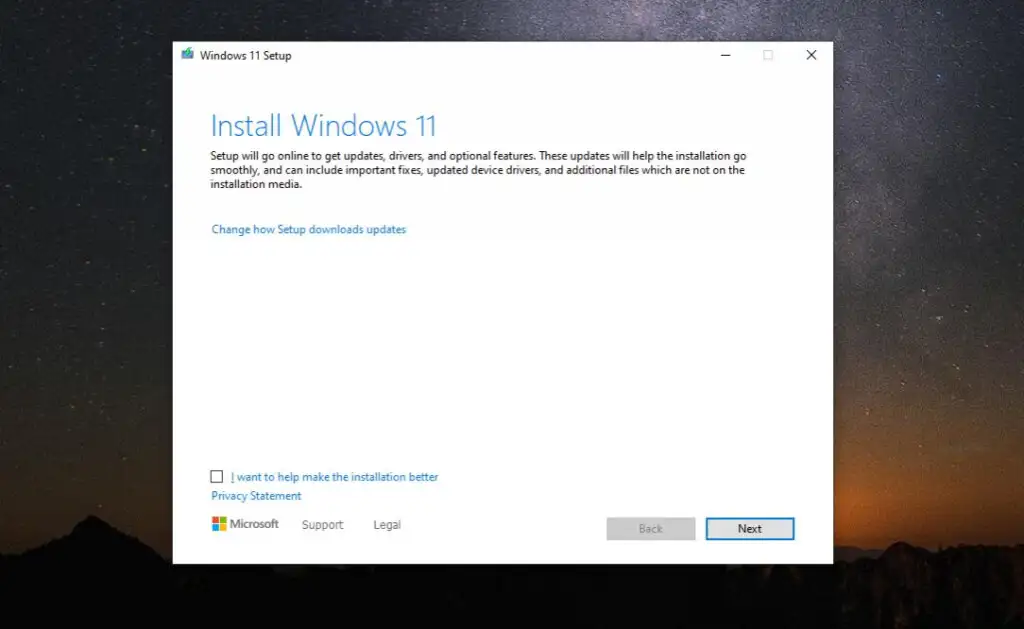
- This initiates the Windows 11 installation wizard. Select Next on the initial screen to continue.
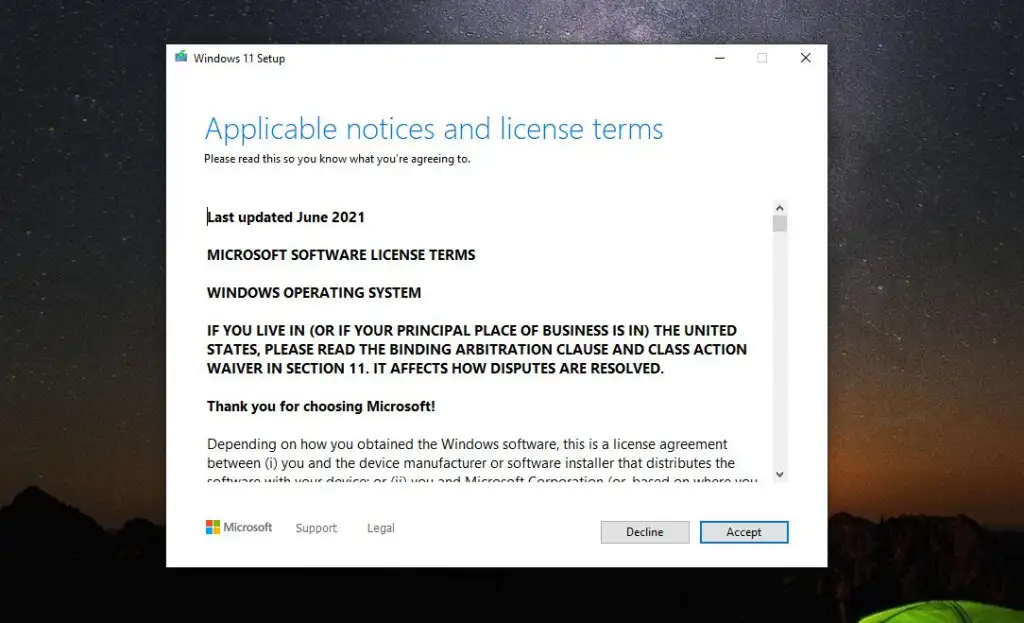
- Scroll through the notices and terms of the license and click Accept.
- The wizard will begin to check for the most recent updates. It may take some time, so please be patient.
- A warning message may appear if your computer does not meet the minimum requirements. Since you already know this, simply select Accept.
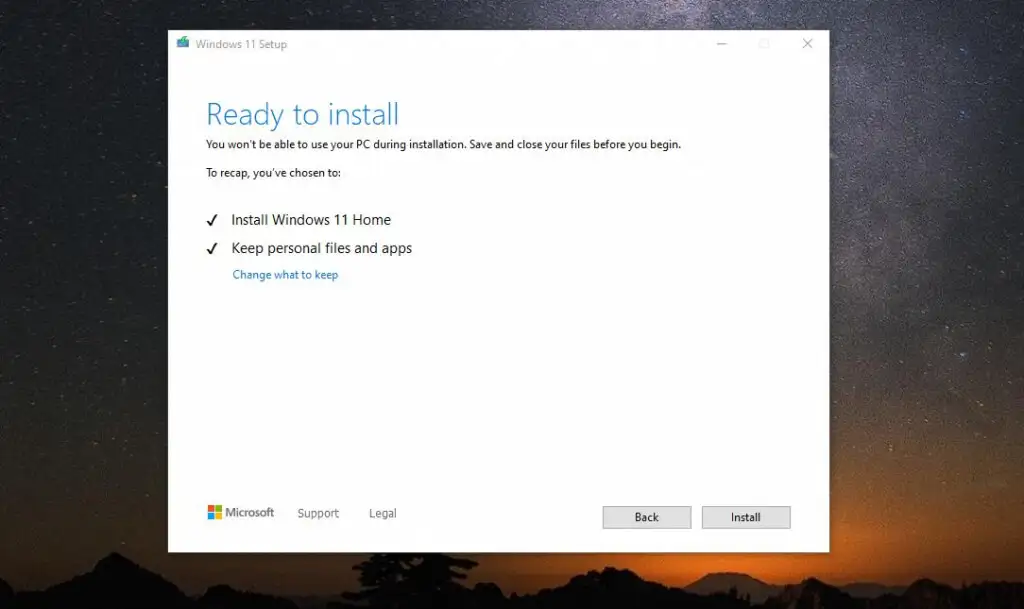
- The Wizard may repeat the process of checking for updates. Finally, the Ready to Install screen will appear. Simply select Install to proceed.
- The final phase of the Windows 11 upgrade requires a great deal of patience. Eventually, the screen will transition to full-screen mode, and the Windows 11 installation will display the percentage of completion. The installation process can take several hours, so leave your computer on and plugged in to ensure that it has power throughout.
Now You Can Use Windows 11!
After the process is complete, your computer will restart, and the Windows 11 login screen will be displayed. Simply enter the Microsoft account credentials you’ve always used to log in to Windows 11, and the new desktop will be displayed.
Now you can enjoy your new operating system just like everyone else!
Have you attempted this procedure and encountered any problems? Do you find Microsoft’s warnings to be unwarranted, or have you experienced issues with Windows 11? Comment your thoughts in the section below.