When it comes to ensuring consistent and reliable fluid flow, particularly in challenging industrial settings, positive displacement pumps (PDPs) are indispensable. From handling high-viscosity materials to operating under extreme temperatures, these pumps maintain a steady flow rate irrespective of changing pressures. This blog explores how positive displacement pumps work, their benefits, and their applications in environments where other pump types struggle to perform.
Fundamentals of Positive Displacement Pumps
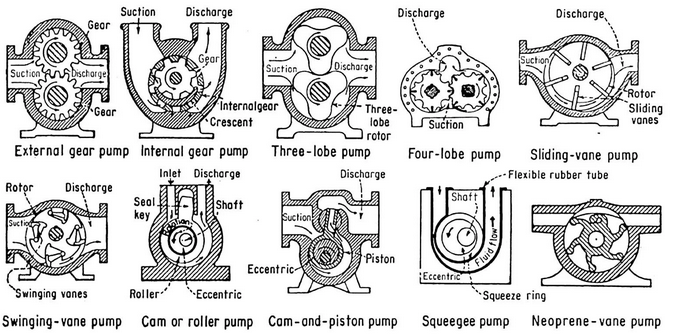
Positive displacement pumps encompass approximately 10 different types, including peristaltic and reciprocating pumps. These pumps operate based on the principle of generating a vacuum to draw fluid into a chamber. As the chamber fills, the pump rotates, which increases the pressure in the system. This pressure then forces the fluid through a discharge port into the pipeline.
The various types of positive displacement pumps can be classified based on the type of motion they utilize. These are categorized into two main types of movement: reciprocating and rotary. Each type of movement plays a critical role in the pump’s operational efficiency and fluid transfer capabilities.
Types of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps (PDPs) are broadly classified into two main categories: rotary pumps and reciprocating pumps. Rotary pumps include gear pumps, lobe pumps, and screw pumps, which are highly effective for the continuous flow of viscous fluids. Their design ensures a steady and controlled movement of liquid, making them ideal for applications requiring smooth and consistent delivery.
On the other hand, reciprocating pumps—such as piston, diaphragm, and plunger pumps—are best suited for high-pressure applications or situations where precise dosing is necessary. These pumps operate through a back-and-forth motion, delivering accurate and controlled fluid displacement.
Operating Principles
Positive displacement pumps (PDPs) generate flow by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it out through the outlet. This process is achieved through mechanical movement, which can involve either rotary or reciprocating motion. Unlike centrifugal pumps, PDPs ensure a consistent and controlled flow, making them ideal for applications requiring precise fluid handling.
The key components of PDPs work together to maintain efficiency and reliability. Chambers are designed to trap the fluid, while rotors or pistons create movement to transfer it through the system. Seals play a crucial role in preventing leaks and ensuring the precision of the pumping process. Each of these components contributes to the pump’s overall functionality, ensuring smooth and reliable operation.
One of the most significant advantages of PDPs is their ability to maintain a consistent flow rate, regardless of pressure variations. This makes them particularly valuable in applications that require accurate and steady fluid transfer, as they provide reliability and efficiency even in changing operational conditions.
Applications in Challenging Environments
These pumps are highly effective in transporting high-viscosity fluids such as oils, syrups, and adhesives. Their ability to maintain a consistent flow prevents blockages, ensuring smooth and efficient industrial processes. This makes them an ideal choice for applications where fluid thickness can cause challenges for other pump types.
Industries that handle abrasive and corrosive materials, such as slurries and chemicals, benefit significantly from PDPs. Their robust design, combined with material options like stainless steel and specialized coatings, enhances durability and resistance to wear, ensuring long-term reliability in harsh operating conditions.
For applications requiring high-pressure fluid delivery, such as hydraulic systems or oil and gas pipelines, reciprocating PDPs provide unmatched reliability. Their precision and ability to maintain consistent pressure make them essential in operations where pressure stability is critical.
Additionally, PDPs excel in extreme temperature conditions, functioning effectively from freezing to boiling temperatures without degradation. Their design ensures consistent performance in environments with significant thermal variations, making them suitable for industries that operate in challenging temperature extremes.
Advantages of Positive Displacement Pumps
Maintaining Flow Uniformity
A defining characteristic of positive displacement pumps (PDPs) is their ability to deliver a uniform flow rate, ensuring consistency across various applications. This makes them particularly valuable in industries such as chemical dosing and food processing, where maintaining a steady and precise flow is essential for quality control and operational efficiency.
Energy Efficiency in Specialized Scenarios
Positive displacement pumps excel in low-flow, high-pressure situations, making them highly energy-efficient for specialized applications. By reducing energy consumption and operational costs, these pumps offer a long-term advantage for industries that require consistent performance without excessive resource expenditure.
Precision in Fluid Transfer
Accuracy in fluid measurement is critical in industries such as pharmaceuticals, where even the slightest deviation can impact product integrity. PDPs provide exceptional precision in fluid transfer, ensuring that every process meets stringent quality standards while maintaining reliability and efficiency.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Preventing clogging in abrasive fluids requires selecting pumps with non-clogging designs and materials that resist wear. Hardened steel or ceramic coatings can significantly enhance durability, ensuring a longer operational lifespan and reducing downtime due to blockages.
- Mitigating wear and tear on components is essential for maintaining efficiency in high-pressure or abrasive environments. Regular maintenance, combined with the right material selection, helps minimize damage, prolonging the life of critical pump parts and improving overall system reliability.
- Ensuring compatibility with corrosive materials is crucial when handling aggressive substances. Utilizing corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or specialized alloys not only extends the pump’s lifespan but also enhances its performance, preventing premature failures due to chemical degradation.
- Maintaining performance in temperature extremes requires specially designed components. Features like advanced seals, thermal insulation, and heat-resistant materials enable pumps to function effectively in both high and low-temperature environments, ensuring consistent operation even under extreme conditions.
Conclusion
These pumps are the backbone of many industrial applications, especially in challenging environments. Their ability to handle high-viscosity materials, maintain uniform flow rates, and operate under extreme conditions makes them indispensable across various industries. By understanding their working principles, applications, advantages, and maintenance best practices, operators can optimize pump performance and longevity.
Whether used for precise fluid transfer, high-pressure applications, or handling abrasive and corrosive materials, PDPs offer reliability and efficiency where other pump types may struggle. Proper selection, regular maintenance, and adherence to best practices will ensure these pumps continue to deliver exceptional performance in demanding settings.